作为模式识别受体(PRRs)中的一员, 在以往研究中NOD样受体(NOD-like receptors,NLRs)家族成员所参与的分子机制研究,更多的集中在其作为炎症小体参与哺乳动物的先天免疫过程中。但也有研究发现,其家族成员例如Nlrp2,Nlrp5(Mater)以及Nlrp7等不仅在哺乳动物生殖系统中高表达,并且在生殖系统中扮演重要的作用,揭示了NLRs所参与的调控网络不仅仅局限于免疫。作为NLR家族中重要的一员,Nlrp14特异高表达与小鼠生殖腺中。但是,至目前为止,尚未有在生理学层面的揭示Nlrp14功能的研究,尤其是Nlrp14在生殖细胞发育方面的机制研究仍旧一面空白。
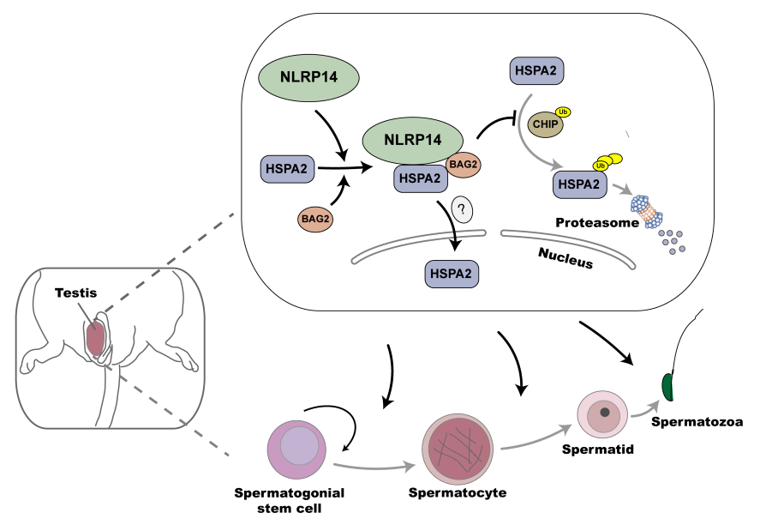
2020年8月,beat365手机官方网站李中瀚教授团队在PNAS在线发表了题为“A non-canonical role of NOD-like receptor NLRP14 in PGCLC differentiation and spermatogenesis”的研究论文。该研究首次揭示了Nlrp14与HSPA2及BAG2形成的复合物抑制HSPA2的泛素化并促使其核转移,进而参与原始生殖细胞样细胞(PGCLCs)分化调控与精子发生过程。该发现揭示了一种由蛋白酶体调控的、非经典的Nlp14功能,为性腺特异性NLRs家族成员在生殖系统发育过程中的分子机制提供全新的视野。beat365手机官方网站助理研究员殷旖珂博士为该论文第一作者,李中瀚教授为通讯作者。
论文链接:www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.2005533117
参考文献
1. Lupfer, C. & Kanneganti, T.D. The expanding role of NLRs in antiviral immunity. Immunological Reviews 255 (2013).
2. Broz, P. & Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nature Reviews Immunology (2016).
3. Kuchmiy, A.A., D’Hont, J., Hochepied, T. & Lamkanfi, M. NLRP2 controls age-associated maternal fertility. Journal of Experimental Medicine 213, 2851-2860 (2016).
4. Peng, H. et al. Nlrp2, a Maternal Effect Gene Required for Early Embryonic Development in the Mouse. Plos One 7, e30344 (2012).
5. Tong, Z.B., Gold, L., Pfeifer, K.E., Dorward, H. & Nelson, L.M. Mater, a maternal effect gene required for early embryonic development in mice. Nature Genetics 26, 267-268 (2000).
6. Murdoch, S. et al. Mutations in NALP7 cause recurrent hydatidiform moles and reproductive wastage in humans. Nature Genetics 38, 300-302 (2006).
7. Davis, C.A. et al. The Encyclopedia of DNA elements (ENCODE): data portal update. Nuclc Acids Research, D1 (2018).
